The human brain is one of the most interesting and complex parts of the body that scientist are still trying to figure out completely. We take for granted our abilities to do things, but do we think about what goes on behind the scenes?
How much do we know about the organ that makes up 2% of our body weight? Did you know that you are prone to different interests and capabilities depending on whether you are left-handed or right-handed? Here are a few facts to get those cells buzzing:
 1 The human brain is the only organ in the human body that lacks nerves despite the fact that it acts as the central command for the central nervous system.
1 The human brain is the only organ in the human body that lacks nerves despite the fact that it acts as the central command for the central nervous system.
This simply implies that the human brain feels no pain.
 2Brain cells can never regenerate. What’s lost is lost forever, like memory loss in the injured and old aged.
2Brain cells can never regenerate. What’s lost is lost forever, like memory loss in the injured and old aged.
The weight of the brain also decreases as we get old.
 3Yawning is the body’s way of cooling down an overheated brain. In addition, when your brain does not receive the appropriate amount of oxygen, the yawn is said to provide the remaining amount of oxygen to the brain.
3Yawning is the body’s way of cooling down an overheated brain. In addition, when your brain does not receive the appropriate amount of oxygen, the yawn is said to provide the remaining amount of oxygen to the brain.
Anoxic brain damage is brain injury caused by a lack of oxygen supply. Without oxygen, brain cells will start to die after four to six minutes.
 4Creating neural pathways and reshaping existing neurons is called neuroplasticity. This is the brain’s way to become more efficient and faster at completing tasks.
4Creating neural pathways and reshaping existing neurons is called neuroplasticity. This is the brain’s way to become more efficient and faster at completing tasks.
As the brain ages through childhood the neural pathways used grow stronger and the pathways less used begin to diminish.
Different tasks rely on different pathways and these pathways have the ability to change and grow—even as an adult.
 5The first sense a human brain learns to detect is touch; however, it takes around 12 weeks to understand the complete feeling.
5The first sense a human brain learns to detect is touch; however, it takes around 12 weeks to understand the complete feeling.
This is the reason the mind can efficiently differentiate between external and self-touch to the body.
 6The brain is suspended in Cerebrospinal fluid, effectively floating in liquid that acts as both a cushion to physical impact (a shock absorber), a barrier to infections, as well as providing the brain with nutrients.
6The brain is suspended in Cerebrospinal fluid, effectively floating in liquid that acts as both a cushion to physical impact (a shock absorber), a barrier to infections, as well as providing the brain with nutrients.
7Exercising is good for your body as well as your brain. If you start exercising, your brain recognizes this as a moment of stress. As your heart pressure increases, the brain thinks you are either fighting the enemy or fleeing from it.
To protect yourself and your brain from stress, you release a protein called BDNF (Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor). This BDNF has a protective and also reparative element to your memory neurons and acts as a reset switch.
That’s why we often feel so fresh after exercising. At the same time, endorphins are released in your brain to minimize the discomfort of exercise and block the feeling of pain.
 8You can make your brain think time is going slowly by doing new things.
8You can make your brain think time is going slowly by doing new things.
When we receive lots of new information, it takes our brains a while to process it all. The longer this processing takes, the longer that period of time feels.
When we’re in life-threatening situations, for instance, “we remember the time as longer because we record more of the experience. Life threatening experiences make us really pay attention, but we don’t gain superhuman powers of perception. Greater attention leads to perception of a longer period of time.”
Conversely, if your brain doesn’t have to process lots of new information, time seems to move faster, so the same amount of time will actually feel shorter than it would otherwise. This happens when you take in lots of information that’s familiar, because you’ve processed it before. Your brain doesn’t have to work very hard, so it processes faster.
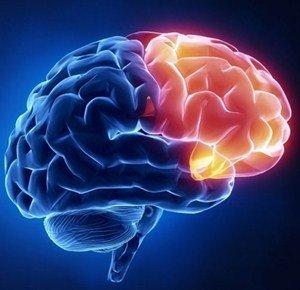 9The frontal lobe (just behind your forehead) is responsible not only for the sense of smell but for emotions and behaviour.
9The frontal lobe (just behind your forehead) is responsible not only for the sense of smell but for emotions and behaviour.
Lose the frontal lobe and we may end up as cruel heartless humans!
 10Learning and thinking takes up more energy from brain cells as opposed to physical activity to the body, hence the hunger while studying.
10Learning and thinking takes up more energy from brain cells as opposed to physical activity to the body, hence the hunger while studying.
You’re probably hungry right now reading this!
Limited free articles. Subscribe for full access.





 Dr. Bilal Philips
Dr. Bilal Philips